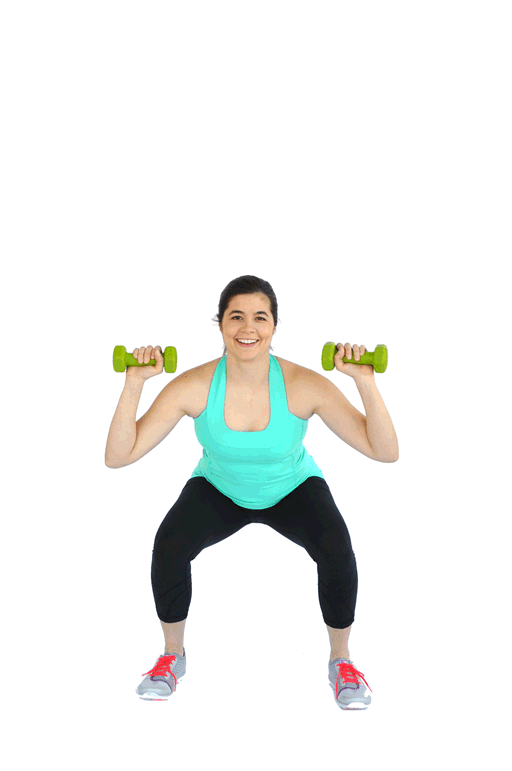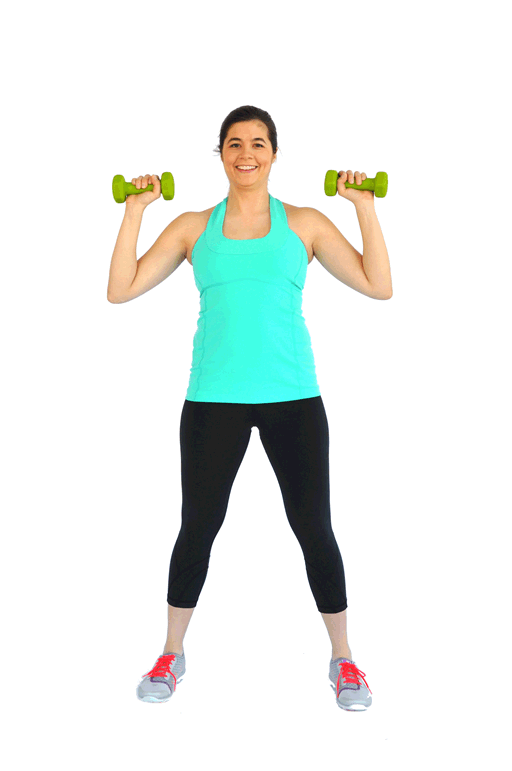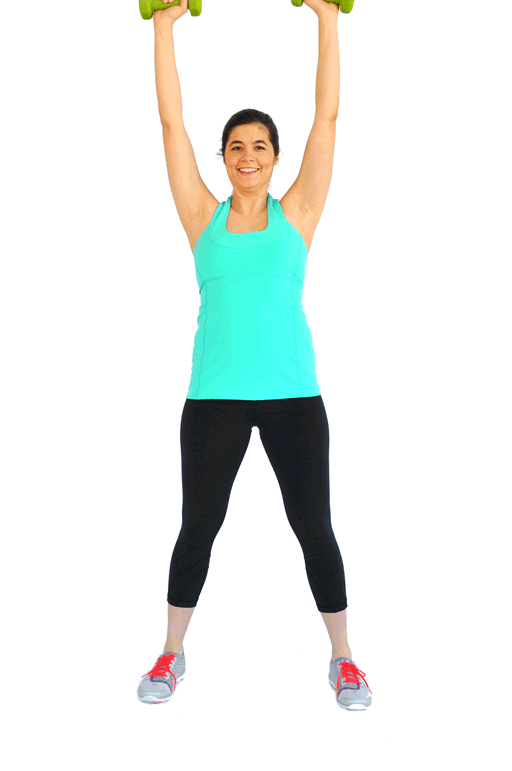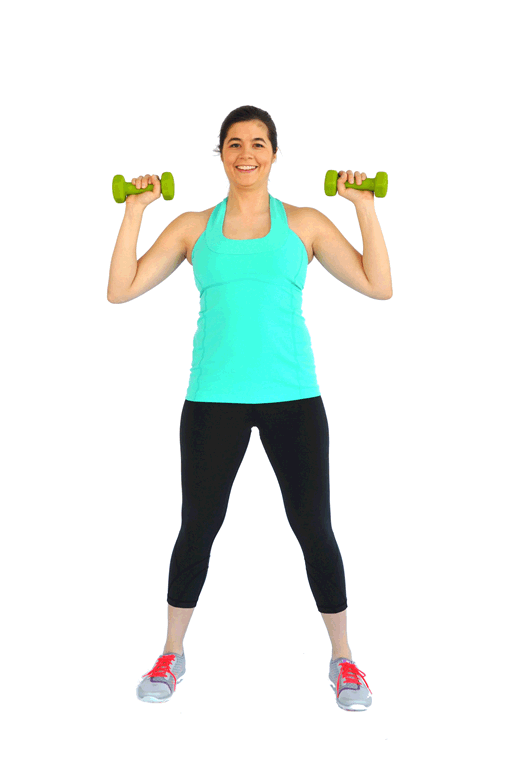Welcome to the ultimate guide on side lunges! If you're looking to supercharge your leg workout routine or simply add a new dimension to your exercise regimen, you've come to the right place. In this comprehensive post, we'll delve into the various aspects of side lunges, exploring their benefits, different variations, common mistakes to avoid, and tips for proper execution. Whether you're a seasoned fitness enthusiast or just starting out, this article is packed with valuable insights to help you master the side lunge and take your fitness to new heights.
What is a Side Lunge?
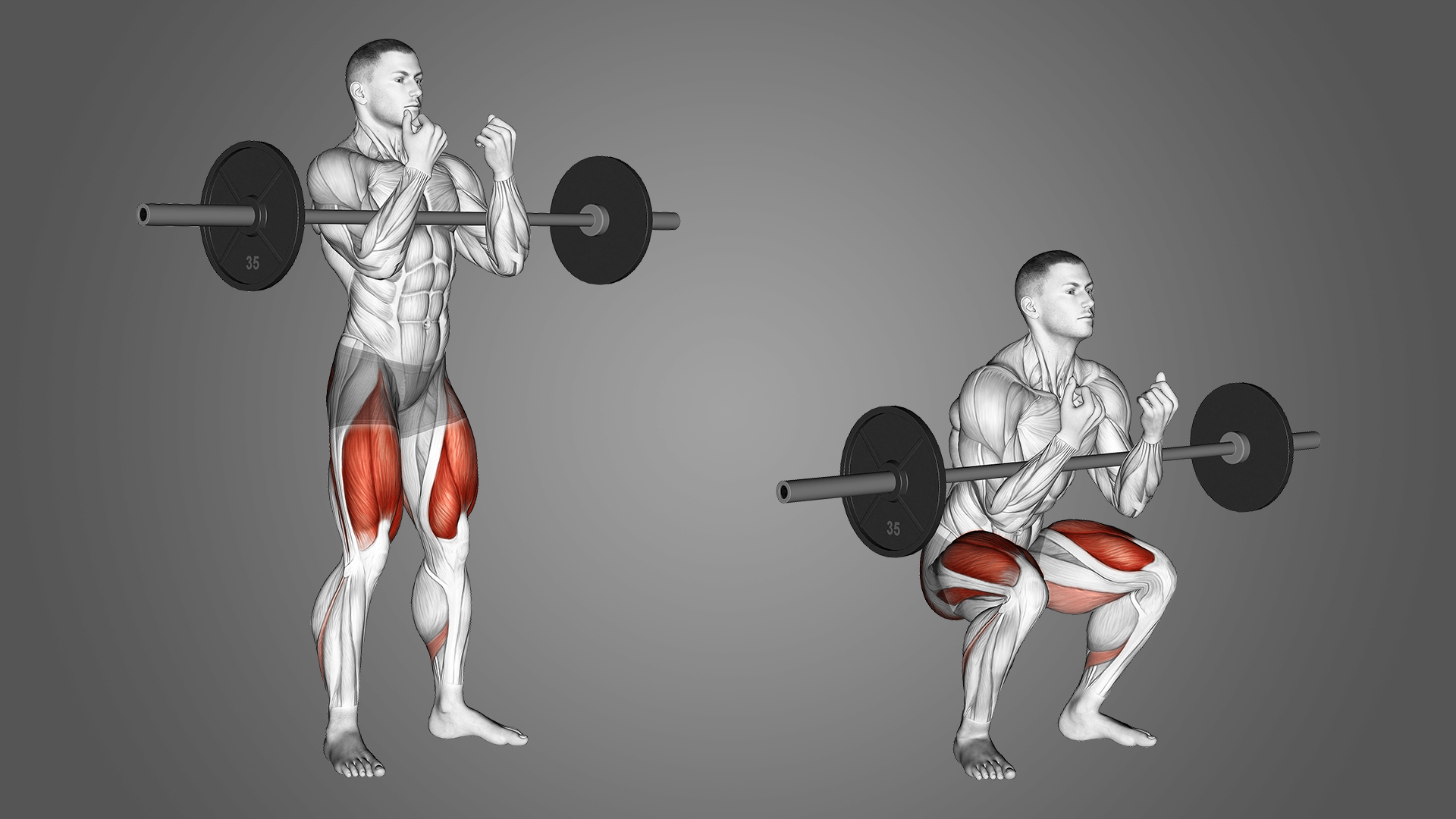
A side lunge, also known as a lateral lunge, is a functional exercise that involves stepping to the side while bending one knee and keeping the other leg straight. This lateral movement engages the muscles of the inner and outer thighs, hips, and glutes, making it an excellent exercise for improving lower body strength, stability, and flexibility.
It targets multiple muscle groups simultaneously. Unlike traditional lunges that involve stepping forward or backward, the side lunge requires stepping to the side, emphasising lateral movement. This unique movement pattern engages the muscles of the inner and outer thighs, hips, and glutes, providing a comprehensive workout for the lower body.
During a side lunge, one leg bends at the knee while the other leg remains straight, allowing for a deep stretch in the inner thigh of the bent leg and a strengthening contraction in the outer thigh and glute of the straight leg. This combination of stretching and strengthening promotes greater flexibility and mobility in the hips and thighs, enhancing overall functional movement patterns.
Muscles Engaged in Side Lunges

The side lunge primarily targets the following muscle groups:
Inner Thighs (Adductors)
As you step to the side and lower your body into the lunge position, the adductor muscles of the inner thighs are engaged to stabilize the movement and control the descent.
Outer Thighs (Abductors)
The abductor muscles of the outer thighs are activated to maintain stability and control as you push off the ground to return to the starting position.
Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Maximus
These muscles, located in the hips and buttocks, play a crucial role in stabilizing the pelvis and controlling the movement of the hips during the side lunge.
Quadriceps
The quadriceps muscles at the front of the thigh work to extend the knee of the bent leg as you lower your body into the lunge position.
Hamstrings
The hamstrings, located at the back of the thigh, assist in bending the knee of the lunging leg and controlling the descent.
By engaging these muscle groups simultaneously, side lunges provide a comprehensive lower body workout that improves strength, stability, and flexibility. Additionally, the lateral movement pattern of side lunges helps to target muscles and movement patterns that may be neglected in traditional forward or backward lunges, making it an effective exercise for overall lower body development.
Why Should You Incorporate Side Lunges into Your Workout Routine?
Side lunges offer a plethora of benefits that make them a valuable addition to any fitness regimen. Incorporating side lunges into your workout routine offers numerous benefits, including:
Improved Lower Body Strength
Side lunges are a highly effective exercise for building lower body strength and muscular endurance. By targeting multiple muscle groups simultaneously, including the thighs, hips, and glutes, side lunges provide a comprehensive workout that challenges the muscles to work together in a coordinated manner. The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, are engaged as you bend your knee and lower your body into the lunge position, while the hamstrings at the back of the thigh assist in controlling the descent. The gluteus medius and gluteus maximus, which are powerful hip extensors, are activated to stabilise the pelvis and control the movement of the hips. By consistently incorporating side lunges into your workout routine, you can gradually increase lower body strength and muscular endurance, leading to improved performance in other activities and reduced risk of injury.
Enhanced Hip Mobility
The lateral movement of side lunges plays a crucial role in promoting greater flexibility and mobility in the hips. Unlike traditional lunges that primarily target forward and backward movement, side lunges require the hips to move in the frontal plane, which helps to stretch and lengthen the muscles surrounding the hip joint. This increased range of motion is essential for performing daily activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs, as well as maintaining proper biomechanics during exercise. By regularly practising side lunges and focusing on deepening the stretch in the hips, you can improve hip mobility and reduce stiffness, leading to greater overall comfort and ease of movement.
Increased Stability and Balance
Performing side lunges requires coordination and balance to maintain proper form throughout the movement. As you step to the side and lower your body into the lunge position, the muscles of the core and lower body work together to stabilise the body and control the descent. This proprioceptive feedback helps to improve balance control and spatial awareness, reducing the risk of falls and injuries in everyday life. Additionally, by challenging your balance in different planes of motion, side lunges can help to strengthen stabilising muscles and improve overall stability, leading to better performance in activities that require dynamic movement and changes in direction.
Glute Activation
Side lunges are highly effective for activating the glute muscles, including the gluteus maximus and gluteus medius. These muscles are crucial for hip stability and overall lower body strength. As you perform side lunges, the gluteus maximus, the largest muscle in the buttocks, contracts to extend the hip joint, driving the movement as you push off the ground to return to the starting position. The gluteus medius, located on the outer surface of the pelvis, works to stabilise the pelvis and control the movement of the hips during the side lunge. By engaging these key muscles, side lunges not only help to strengthen the glutes but also promote better hip stability and alignment, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall lower body function.
Core Engagement
In addition to targeting the glute muscles, performing side lunges requires significant core engagement to maintain balance and proper form throughout the movement. The core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis, work together to stabilise the torso and pelvis, preventing excessive tilting or rotation during the lunge. This core stability not only improves balance and coordination but also leads to enhanced core strength and stability over time. By incorporating side lunges into your workout routine, you can effectively strengthen the muscles of the core, leading to better posture, reduced risk of lower back pain, and improved overall functional movement.
Overall, side lunges are a highly effective exercise for targeting multiple muscle groups in the lower body and improving strength, stability, and flexibility. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced athlete, incorporating side lunges into your workout routine can help you achieve your fitness goals and enhance your overall physical performance.
How to Perform a Side Lunge
Performing a side lunge correctly is essential to maximise its benefits and minimise the risk of injury. Follow these steps to perform a proper side lunge:
Starting Position
- Begin by standing tall with your feet hip-width apart. This position provides a stable base from which to initiate the movement. Keep your arms relaxed at your sides to maintain balance and stability throughout the exercise.
Step to the Side
- Next, initiate the side lunge by taking a wide step to the right with your right foot. As you step to the side, focus on keeping your toes pointing forward to ensure proper alignment of the lower body. This will help engage the correct muscle groups and prevent strain on the knees and hips.
Bend the Knee
- Once you've stepped to the side, shift your body weight onto your right foot as you bend your right knee. Lower your body toward the ground, keeping your left leg straight. Aim to lower your body until your right thigh is parallel to the ground, ensuring a deep stretch in the inner thigh of the bent leg.
Return to Starting Position
- To complete the side lunge, push off your right foot and return to the starting position by straightening your right leg and bringing your left foot back to the center. Focus on engaging the muscles of the inner and outer thighs, hips, and glutes as you push off the ground to generate power and momentum.
Repeat on the Other Side
- Once you've completed the side lunge on the right side, repeat the same movement on the left side. Take a wide step to the left with your left foot, keeping your toes pointing forward, and bend your left knee while keeping your right leg straight. Lower your body toward the ground, then push off your left foot to return to the starting position.
- By following these steps and paying attention to proper form and technique, you can perform side lunges safely and effectively, maximizing their benefits for your lower body strength, stability, and flexibility. Remember to maintain control throughout the movement, and avoid rushing or using momentum to ensure optimal results. As you become more comfortable with the exercise, you can gradually increase the intensity by adding resistance or incorporating advanced variations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While side lunges are an effective exercise, several common mistakes can compromise their effectiveness and increase the risk of injury. Avoid these common mistakes when performing side lunges:
- Incorrect Foot Placement,Ensure that your feet are hip-width apart and your toes are pointing forward to maintain proper alignment and stability.
- Knee Alignment, Avoid allowing your knees to collapse inward during the lunge, as this can strain the knee joint. Keep your knees aligned with your toes throughout the movement.
- Improper Hip Hinge, Maintain a slight bend in your hips and knees throughout the movement to prevent excessive strain on the hip and knee joints.
- Spinal alignment,Leaning too far forward or backward, which can compromise spinal alignment and stability.
- Engaging the core muscles,Failing to engage the core muscles, which are essential for maintaining balance and proper form.
Variations of Side Lunges
To add variety to your workout routine and target different muscle groups, consider incorporating variations of the side lunge such as:
- Weighted side lunges, One way to increase the intensity of side lunges is by adding resistance with weights. Hold dumbbells or a kettlebell in each hand also you can add resistance by wearing weighted vests while performing side lunges to increase the workload on your muscles. The added resistance challenges your strength and endurance, helping to build lean muscle mass and improve overall strength. Be sure to choose weights like that are challenging but still allow you to maintain proper form throughout the movement.
- Curtsy lunges, are a variation of the traditional side lunge that adds a cross-behind motion to target the inner thighs and glutes. To perform a curtsy lunge, step your right foot behind your left foot at a diagonal angle, keeping your toes pointing forward. Bend both knees as if curtsying, lowering your body toward the ground while maintaining an upright posture. Push off your right foot to return to the starting position, then repeat on the other side. Curtsy lunges provide a unique challenge to the lower body and help sculpt the inner thighs and glutes.
- Reverse lunges with a lateral raise, Combine a reverse lunge with a lateral arm raise to engage the shoulders and arms while working the lower body.
Tips for Maximising Your Side Lunge Workout
To maximise the effectiveness of your side lunge workout and achieve optimal results, consider the following tips:
- Proper Weight Distribution, Shift your body weight onto the heel of the lunging leg to engage the glutes and hamstrings effectively.
- Correct Hip and Knee Positioning, Ensure that your hips and knees are in line with each other and avoid allowing your knees to extend beyond your toes during the lunge.
- Engaging the Core, Focus on engaging your core muscles throughout the movement to maintain stability and control, which will help prevent injury and improve overall strength.
- Mindful Movement, Focus on controlled, deliberate movements throughout the entire range of motion. Avoid rushing through the exercise, and instead, concentrate on engaging the targeted muscles with each repetition.
- Breathing Technique, Coordinate your breathing with your movements to optimise oxygen flow and energy distribution. Inhale deeply as you lower into the lunge and exhale forcefully as you push back to the starting position. This rhythmic breathing pattern helps stabilise your core and enhances overall performance.
- Progressive Overload, As your strength and endurance improve, challenge yourself by gradually increasing the intensity of your side lunges. You can do this by incorporating resistance bands, holding onto dumbbells or kettlebells, These variations add an extra dimension of difficulty, forcing your muscles to work harder and adapt to new stimuli.
- Balance and Stability, Pay attention to your balance and stability throughout the movement. If you find it challenging to maintain stability, try performing the exercise near a wall or using a chair for support until you feel more confident. Engaging your core muscles and focusing on a fixed point in front of you can also help improve balance and stability.
- Consistency is Key, Like any exercise, consistency is key to seeing results. Aim to incorporate side lunges into your workout routine at least two to three times per week, gradually increasing the number of repetitions and sets as you progress. By staying consistent and challenging yourself regularly, you'll continue to build strength, improve endurance, and enhance overall fitness.
Incorporating these tips into your side lunge workout routine will help you maximise the benefits of this dynamic exercise and achieve your fitness goals more efficiently. Remember to start slowly and gradually increase the intensity as you build strength and confidence.
Side Lunges for Beginners
If you're new to side lunges, start with bodyweight exercises and gradually increase the intensity as you build strength and confidence. Focus on mastering the proper form and alignment before progressing to more challenging variations.
Some Tips for Beginners
- Start with Bodyweight, Begin with bodyweight side lunges to master the movement pattern and build strength.
- Focus on Form, Pay attention to proper form and alignment, keeping your chest lifted, spine neutral, and core engaged.
- Gradually Increase Intensity, Progress slowly by adding more repetitions, sets, or resistance over time.
- Breathe Properly, Inhale as you lower into the lunge, exhale as you push back to the starting position.
- Be Patient, Building strength takes time, so stay patient and consistent with your practice.
Beginner Circuit Training Workout Plan
Perform each exercise for 30 seconds, followed by a 30-second rest. Complete the circuit 2-3 times with a 1-2 minute rest between circuits.
Cool Down and Stretch
After completing the circuit, take a few minutes to cool down and stretch your muscles. Focus on stretching the muscles worked during the workout, including the legs, hips, chest, and core.
Incorporate this beginner-friendly circuit training workout plan into your fitness routine 2-3 times per week, gradually increasing the intensity as you progress. Stay consistent, listen to your body, and enjoy the journey as you build strength, improve mobility, and work toward your fitness goals with side lunges and other exercises.
Conclusion
Side lunges are a versatile and effective exercise that can help you achieve your fitness goals and enhance your overall well-being. By incorporating side lunges into your workout routine and paying attention to proper form and technique, you can strengthen your lower body, improve balance and stability, and reduce the risk of injury. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced athlete, side lunges offer a multitude of benefits that make them a valuable addition to any fitness regimen.
Side lunges primarily target the muscles of the lower body, including the thighs, hips, and glutes. By consistently performing side lunges with proper form and technique, you can strengthen these muscle groups, leading to improved lower body strength and muscular endurance. Additionally, side lunges engage stabilising muscles, which helps improve balance and stability, crucial for preventing falls and injuries, especially as you age.
Remember, consistency is key to seeing results, so make sure to incorporate side lunges into your workouts regularly and challenge yourself with different variations and intensities. Whether you're aiming to build strength, improve balance, or enhance flexibility, side lunges can be tailored to suit your needs and preferences. With dedication and perseverance, you'll unlock the full potential of side lunges and take your fitness to new heights. So, make side lunges a regular part of your fitness routine and watch as you achieve remarkable progress and results.