The latissimus dorsi, or "lats," play a crucial role in upper body strength, posture, and athletic performance. These large back muscles contribute to pulling power, shoulder stability, and overall functional movement. Kettlebell lat exercises offer a dynamic and versatile way to train the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and trapezius muscles enhancing both strength and mobility. This guide covers the best kettlebell exercises for lat development, their benefits, a sample workout routine, common mistakes to avoid, and expert tips for maximizing muscle growth.
Anatomy of the Lats & Why They Matter
The latissimus dorsi is a broad, fan-shaped muscle that extends from the lower back to the upper arm. It is responsible for movements such as pulling, rowing, and shoulder extension. Strong lats contribute to:
-
Improved posture and spinal support.
-
Enhanced athletic performance in sports like swimming, climbing, and rowing.
-
Reduced risk of injury by stabilizing the shoulders and spine. Kettlebell training provides a unique advantage over machines and barbells due to its requirement for engagement, stabilization, and dynamic movement
Benefits of Training Lats with Kettlebells
Kettlebell lat training improves strength, mobility, and grip, enhancing both athletic performance and daily movement. It improves grip, pulling power and flexibility, benefiting both athletic performance and everyday movement.
-
Enhances Grip Strength and Pulling Power: Kettlebell exercises like rows and swings challenge grip endurance by requiring sustained tension. Stronger grip and pulling muscles improve performance in deadlifts, pull-ups, rock climbing, and daily tasks like carrying heavy objects.
-
Develops Functional Strength: Kettlebell lat training mimics real-life movement patterns, : reinforcing pulling, lifting, and carrying mechanics. This improves practical strength for activities like moving furniture, loading groceries, and playing sports requiring upper-body endurance.
-
Improves Mobility and Flexibility: Dynamic kettlebell movements promote a greater range of motion in the shoulders, back, and spine. Increased lat flexibility enhances posture, reduces stiffness, and lowers the risk of injuries caused by restricted movement.
-
Strengthens the Core: Many kettlebell exercises, such as renegade rows and Turkish get-ups, demand stabilization. Engaging the lats improves balance, enhances spinal support, and builds full-body coordination for athletic and daily activities.
Kettlebell Exercises for Lats
Training the lats with kettlebells builds strength, stability, and functional movement. These exercises target multiple muscle groups, improving pulling power, grip strength, and mobility for enhanced athletic performance and everyday activities.
Kettlebell Rows
Kettlebell rows primarily target the upper back (rhomboids, lats and traps), middle back and biceps while also reinforcing posture, balance and core stability. They improve pulling power, enhance muscle coordination, and help prevent imbalances by strengthening each side of the body independently.
1. Single-Arm Bent-Over Row
This unilateral exercise isolates each lat, ensuring balanced muscle growth. It enhances back strength and pulling mechanics, reducing injury risks while improving posture, grip endurance, and overall functional strength.
How to Perform:
-
Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a kettlebell in one hand.
-
Hinge at the hips, keeping your back straight.
-
Pull the kettlebell toward your ribs, squeezing your lat at the top.
-
Lower it slowly to maintain control. Repeat on both sides.
2. Renegade Row
A challenging movement performed in a plank position, engaging the lats, shoulders. It strengthens the back while improving anti-rotational stability, benefiting athletes and those needing greater balance and control.
How to Perform:
-
Begin in a push-up position with a kettlebell in each hand.
-
Keep your body in a straight line, avoiding excessive hip rotation.
-
Row one kettlebell toward your ribs while stabilizing with the other arm.
-
Lower slowly and repeat on the opposite side.
3. Gorilla Row
This two-kettlebell movement mimics barbell rows but offers a greater range of motion. It enhances lat activation, grip endurance, and pulling power while reinforcing core engagement for stability and overall upper-body strength.
How to Perform:
-
Stand with feet wider than shoulder-width, kettlebells between your feet.
-
Hinge at the hips and keep your back straight.
-
Row one kettlebell explosively while keeping the other planted.
-
Lower and alternate between sides, maintaining control throughout.
Kettlebell Swings
Kettlebell swings develop explosive power by dynamically engaging the lats. The movement improves grip, posture, and core control while reinforcing proper hip drive mechanics, reducing lower back strain, and increasing endurance.
How to Perform:
-
Keep your arms tight to your body, actively pulling the kettlebell back during the descent.
-
Engage the lats by controlling the downward motion instead of letting the weight drop passively.
-
Focus on driving the hips forward while maintaining a strong, braced core.
Kettlebell Deadlifts & High Pulls
Both exercises strengthen the posterior chain, including the lats. They improve fitness, pulling power, grip endurance, and posture, reinforcing hip hinge mechanics and developing explosive strength necessary for athletic and functional movements.
1. Kettlebell Deadlifts
A fundamental movement that builds posterior strength while activating the lats for stability. It enhances lower back health, grip control, and coordination, translating to improved power in lifts and daily movements.
How to Perform:
-
Stand with feet hip-width apart, kettlebell between your feet.
-
Hinge at the hips, keeping your back straight and shoulders engaged.
-
Grip the kettlebell, drive through your heels, and stand tall.
-
Lower it with control, maintaining tension in the lats.
2. High Pulls
An explosive movement that strengthens the lats while improving shoulder mobility and pulling mechanics. It enhances power generation, grip strength, and athletic performance by combining controlled pulling with hip drive coordination.
How to Perform:
-
Start with a kettlebell swing but pull the weight higher toward your chest.
-
Keep the elbows high and close to your body.
-
Control the descent back into a swing position.
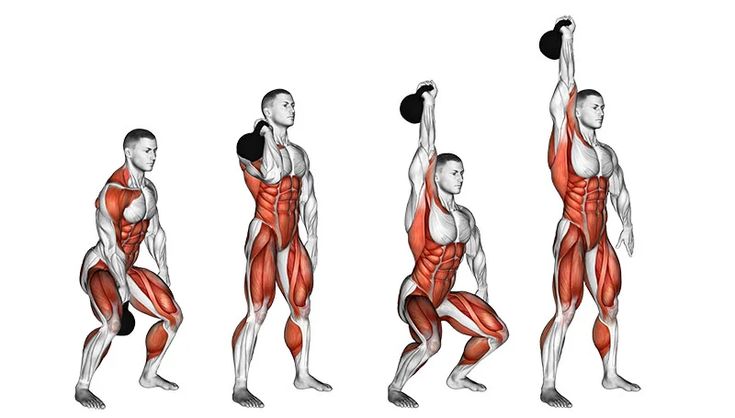
Kettlebell Snatch
This full-body exercise develops lat endurance, power, and coordination. It strengthens shoulder stability, enhances grip strength, and improves cardiovascular conditioning while reinforcing dynamic control over explosive overhead movements.
How to Perform:
-
Begin with a kettlebell swing, then pull the kettlebell overhead in one fluid motion.
-
Lock out the kettlebell at the top with a stable shoulder position.
-
Lower with control, bringing the kettlebell back into the swing position.
Kettlebell Pullover
A classic isolation exercise for lat strength and flexibility. It enhances shoulder mobility, improves upper-body coordination, and reinforces the mind-muscle connection by stretching and contracting the lats through an extended range of motion.
How to Perform:
-
Lie flat on a bench or the ground, holding a kettlebell with both hands.
-
Lower the kettlebell behind your head, keeping arms extended.
-
Bring it back overhead, engaging the lats throughout the movement.
Kettlebell Windmill
A mobility-focused movement that strengthens the lats, core, and shoulders. It enhances rotational stability, improves flexibility, and promotes functional strength, making it beneficial for injury prevention and dynamic sports performance.
How to Perform:
-
Hold a kettlebell overhead with one arm.
-
Keep your legs straight, hinge at the hips, and lower your torso sideways.
-
Touch your opposite hand to the floor while keeping the kettlebell stable overhead.
Kettlebell Archer Row
An advanced unilateral exercise that enhances lat activation, coordination, and control. It builds pulling strength while promoting a greater range of motion, improving balance, and reinforcing core stability for overall muscle development, while also engaging the lateral stabilizers, obliques, and shoulder muscles for enhanced functional strength.
How to Perform:
-
Assume a wide stance with a kettlebell in each hand.
-
Row one kettlebell toward your ribs while extending the other arm outward.
-
Control the movement and engage your lats fully.
Kettlebell Lat Workout Routine:
1. Warm-Up: Preparing the Body for Training
A proper warm-up improves muscle activation, flexibility, and injury prevention while ensuring smooth movement execution. It targets the shoulders, thoracic spine, and posterior chain for optimal lat engagement.
-
Shoulder mobility drills
-
Arm circles and thoracic rotations
-
Light kettlebell swings and deadlifts
2. Workout Plan: Lat-Strengthening Kettlebell Routine
Divided into Beginner, Intermediate, and Advanced levels, this workout progressively increases difficulty, building lat strength, endurance, and mobility for enhanced athletic performance.
Beginner:
Beginners focus on lat activation, proper form, and endurance while developing coordination for progressing to advanced movements safely.
-
Single-Arm Bent-Over Row – 3x10 (each arm)
-
Kettlebell Deadlift – 3x12
-
Kettlebell Swing – 3x15
Intermediate:
Intermediate exercises introduce dynamic pulling movements, core engagement, and rotational control, improving lat strength, endurance, and functional movement patterns.
-
Renegade Row – 3x8 (each arm)
-
Gorilla Row – 3x10
-
High Pull – 3x12
-
Kettlebell Windmill – 3x8 (each side)
Advanced:
Advanced exercises incorporate explosive movements, heavier resistance, and multi-muscle engagement, maximizing lat strength, endurance, and functional power.
-
Kettlebell Snatch – 3x6 (each arm)
-
Archer Row – 3x10 (each arm)
-
Kettlebell Pullover – 3x12
-
Heavy Kettlebell Swings – 3x15
3: Cooldown & Recovery:
A structured cooldown prevents stiffness, enhances flexibility, and reduces muscle soreness, promoting long-term strength gains and injury prevention.
-
Lat and shoulder stretches
-
Foam rolling to reduce muscle tension
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Training
Mistakes in kettlebell training can lead to inefficient muscle activation, poor progress, and injuries. Avoiding these errors ensures better lat engagement, improved strength gains, and long-term training success.
-
Using Excessive Weight at the Cost of Proper Form: Lifting too heavy causes compromised technique, reduced range of motion, and poor muscle activation. Excessive weight strains joints and ligaments, increasing injury risk. Prioritizing proper form, control, and gradual progression ensures safe and effective strength development.
-
Neglecting Scapular Control: Failing to control the scapula (shoulder blades) reduces lat activation and limits pulling strength. Poor scapular positioning leads to shoulder instability and strain, increasing injury risk. Focusing on scapular retraction and engagement improves movement efficiency and muscle activation.
-
Over-Reliance on Arms Instead of Engaging the Lats: Many lifters pull with their arms rather than engaging the lats, limiting back development. Overuse of the biceps and forearms leads to early fatigue and poor movement efficiency. Initiating pulls from the lats with elbow-driven movement ensures maximum muscle engagement.
-
Poor Posture Leading to Lower Back Injuries: A rounded or excessively arched back places unnecessary strain on the spine and lower back muscles, increasing injury risk. Maintaining a neutral spine, engaged core, and stable posture ensures safer execution, better power transfer, and long-term progress.
Pro Tips for Maximizing Lat Growth with Kettlebells
Building strong and well-developed lats requires more than just lifting weights. By adjusting tempo, grip variations, and progressively overloading muscles, you can optimize muscle engagement, enhance growth, and improve overall back strength.
-
Use Tempo and Time Under Tension: Slowing down kettlebell movements increases time under tension (TUT), forcing the lats to work harder. Controlled eccentric (lowering) and concentric (lifting) phases enhance muscle activation, improve endurance, and promote hypertrophy. Focusing on slower, controlled reps builds stronger, more resilient lats while reducing momentum-based lifting.
-
Experiment with Grip Variations: Using different grip variations activates various parts of the lats, improving overall development. A wide grip emphasizes upper lats, a neutral grip targets mid-back stability, and an underhand grip shifts focus toward the lower lats. Switching grips in exercises like rows, high pulls, and deadlifts ensures well-rounded growth.
-
Incorporate Progressive Overload: Gradually increasing weight, reps, or intensity ensures consistent muscle growth and strength gains. Without progressive overload, the lats adapt and stop developing. Slowly adding resistance, extending sets, or reducing rest periods forces the muscles to continuously adapt and strengthen, leading to better performance and enhanced lat definition.
FAQs About Kettlebell Lat Workouts
Q: Can kettlebells replace pull-ups for lat training?
While kettlebells are effective for lat development, pull-ups remain a top exercise for building back strength. Combining both is ideal.
Q: How often should I train my lats with kettlebells?
2-3 times per week, depending on your recovery and overall training split.
Q: What kettlebell weight should beginners use for lat exercises?
Start with a 12-16kg (26-35lb) kettlebell and increase the weight as your strength improves, following your coach’s advice.
Q: Are kettlebells effective for building wide lats?
Yes, particularly when combined with progressive overload and proper form.
Q: What are the best kettlebell exercises for lats if I have limited space?
Kettlebell rows, pullovers, and windmills require minimal space while delivering great results.
References:
Anatomy and Importance of Lats
National Academy of Sports Medicine (NASM). (n.d.). Latissimus Dorsi: Anatomy and Function. Retrieved from https://www.nasm.org
Benefits of Training Lats with Kettlebells
-
American Council on Exercise (ACE). (n.d.). Benefits of Functional Training with Kettlebells. Retrieved from https://www.acefitness.org
-
Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Strength Training: How to Get Stronger, Leaner, Healthier. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org
Kettlebell Exercises for Lats
-
Pavel Tsatsouline. (2001). The Russian Kettlebell Challenge: Xtreme Fitness for Hard Living Comrades. Dragon Door Publications.
-
StrongFirst. (n.d.). Kettlebell Training Principles. Retrieved from https://www.strongfirst.com
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Training
-
American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM). (n.d.). Strength Training Guidelines. Retrieved from https://www.acsm.org
-
Men’s Health. (n.d.). Kettlebell Basics: Best Practices for Beginners. Retrieved from https://www.menshealth.com