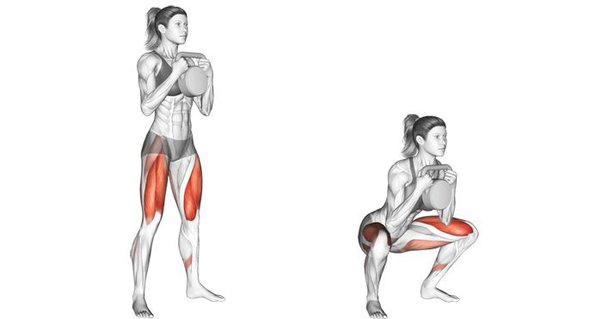
The goblet squat is a highly effective and versatile exercise that has gained popularity for its ability to improve lower body strength, enhance core stability, and promote proper squat mechanics. By holding a weight close to your chest, the goblet squat engages a variety of muscle groups, making it a valuable addition to any fitness routine. In this article, we will delve into the muscles worked during a goblet squat, the correct technique, and the benefits of incorporating this exercise into your workouts.
Understanding Goblet Squat
The goblet squat is a type of squat where a weight (usually a dumbbell or kettlebell) is held close to the chest with both hands. This exercise is known for its simplicity and effectiveness in improving squat mechanics and lower body strength.
The goblet squat represents a versatile and effective variation of the traditional squat exercise. In this technique, a weight, typically a dumbbell or kettlebell, is firmly gripped close to the chest with both hands. This exercise stands out for its simplicity and accessibility, making it suitable for individuals of all fitness levels. One of its key benefits lies in its ability to improve squat mechanics by promoting an upright torso and proper knee alignment. By engaging major lower body muscle groups such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, the goblet squat effectively builds strength and muscle mass in these areas. Additionally, the need to stabilize the weight in front of the body engages the core muscles, further enhancing core strength and stability. Its versatility allows it to be incorporated as a warm-up, main lift, or accessory movement in various workout routines. Overall, the goblet squat offers a comprehensive lower body workout while also promoting proper form and functional fitness.
Purpose of Goblet Squat
The goblet squat aims to develop lower body strength, improve core stability, and enhance overall squat form. It is an excellent exercise for beginners to learn proper squat mechanics and for advanced athletes to refine their technique and add variety to their training.
The purpose of the goblet squat extends beyond just building lower body strength; it encompasses improving core stability and enhancing overall squat form. By holding the weight close to the chest, this exercise challenges the core muscles to maintain stability throughout the movement, promoting a strong and balanced core. Additionally, the goblet squat serves as an invaluable tool for individuals of all fitness levels, offering beginners the opportunity to learn proper squat mechanics and advanced athletes the chance to fine-tune their technique and introduce variety into their training regimen. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a staple in any well-rounded fitness program, contributing to improved strength, stability, and functional movement patterns.
Muscles Targeted During Goblet Squat

The goblet squat engages several muscle groups, making it a comprehensive exercise for lower body and core strength.
Quadriceps
Role of Quadriceps in Goblet Squat
The role of the quadriceps in the goblet squat is pivotal, as these muscles are primarily responsible for knee extension throughout the movement. Situated at the front of the thigh, the quadriceps are heavily engaged during both the lowering and rising phases of the squat. As you descend, they work to control the movement and support the lowering of the body, while during the ascent, they contract to extend the knees and propel you back to the starting position. The activation of the quadriceps not only strengthens these muscles but also contributes to the overall stability and effectiveness of the goblet squat, making it a comprehensive lower body exercise.Additional exercises for strengthening the quadriceps include lunges, leg presses, and step-ups.
Glutes
Activation of Glutes During Goblet Squat
In the goblet squat, the activation of the glutes is fundamental to the movement, particularly during the ascent phase. As you rise from the squat position, the gluteal muscles are heavily engaged to extend the hips and drive the body upward. This activation not only contributes to the strength and power generated during the movement but also plays a crucial role in maintaining hip stability throughout the exercise. By targeting the glutes, the goblet squat effectively strengthens these key muscles, enhancing overall lower body strength and stability while promoting proper movement mechanics.To further strengthen the glutes, incorporate exercises such as hip thrusts, glute bridges, and deadlifts into your routine.
Core Muscles
Engagement of Core Muscles in Goblet Squat
During the goblet squat, the engagement of core muscles is essential for maintaining stability and proper form throughout the movement. The rectus abdominis, obliques, and erector spinae work in synergy to stabilize the torso and prevent excessive forward lean or rounding of the back. By holding the weight close to the chest, the core muscles are challenged to maintain an upright posture, thus strengthening the core and improving overall stability. This activation not only enhances the effectiveness of the goblet squat but also translates to better performance in other exercises and daily activities, emphasizing the importance of core strength in functional movement.
Planks, Russian twists, and leg raises are effective exercises to strengthen the core muscles.
Hamstrings
Involvement of Hamstrings in Goblet Squat
In the goblet squat, the involvement of the hamstrings plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and stability throughout the exercise. As the descent begins, the hamstrings engage to control the lowering phase, ensuring a smooth and controlled movement pattern. Additionally, their contribution to leg stability helps prevent excessive forward lean and supports proper alignment of the knees and hips. While the primary focus may be on the quadriceps and glutes, the activation of the hamstrings adds depth and effectiveness to the goblet squat, making it a comprehensive lower body exercise that targets multiple muscle groups simultaneously.
Include exercises like Romanian deadlifts, hamstring curls, and good mornings to target the hamstrings.
Calves
Contribution of Calves in Goblet Squat
In the goblet squat, the contribution of the calf muscles is notable, especially during the lower phase of the movement. While the primary emphasis lies on the larger muscle groups such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, the calves play a crucial role in stabilizing the legs and maintaining balance, particularly at the bottom of the squat. Their activation helps ensure proper alignment of the ankles and supports the overall stability of the lower body throughout the exercise. Though the calf muscles may not be the primary focus of the goblet squat, their involvement underscores the importance of a well-rounded approach to lower body training.
Calf raises and seated calf presses are excellent for building calf strength.
How to Perform a Goblet Squat
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9TOlFFKzWO0
To perform a goblet squat, follow these steps:
Start Position
Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart. Hold a dumbbell or kettlebell close to your chest with both hands, ensuring your elbows point downwards and the weight is secure.
Lowering Phase
Engage your core and begin to lower your body by bending at the hips and knees. Keep your chest lifted and back straight. Aim to lower yourself until your thighs are parallel to the ground or as low as your flexibility allows.
Bottom Position
At the bottom of the squat, your elbows should be inside your knees, and your knees should track over your toes.
Rising Phase
Push through your heels to return to the starting position, straightening your legs and standing up tall. Maintain the weight close to your chest throughout the movement.
Benefits of the Goblet Squat
Incorporating the goblet squat into your workout routine offers numerous benefits:
- Improves Squat Form, The goblet squat encourages proper squat mechanics, making it an excellent exercise for beginners. The positioning of the weight helps maintain an upright torso and correct knee tracking.
- Core Strengthening, Holding the weight close to your chest engages your core muscles, providing an effective workout for your midsection. A strong core is essential for overall stability and injury prevention.
- Lower Body Strength, The goblet squat effectively targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, building strength and endurance in these muscle groups. This can enhance performance in other exercises and daily activities.
- Versatility, The goblet squat can be performed with various weights, making it suitable for different fitness levels. You can easily adjust the difficulty by increasing or decreasing the weight.
- Functional Fitness, The movement pattern of the goblet squat mimics everyday activities, such as lifting and bending, enhancing overall functional strength. This translates to improved performance in daily tasks and sports.
Safety Tips for Goblet Squat
Ensuring safety during goblet squats is crucial for preventing injuries and maximizing the effectiveness of the exercise. Here are detailed safety tips to consider:
- Proper Form, Maintaining proper form is essential for safety and effectiveness during goblet squats. Keep your torso upright throughout the movement, avoiding any rounding of the back. Engage your core muscles to stabilize the spine and maintain a neutral position.
- Controlled Movements, Perform goblet squats with controlled and deliberate movements. Avoid rapid or jerky motions, as they can increase the risk of strain or injury to muscles and joints. Focus on maintaining tension in the targeted muscles throughout the entire range of motion. This controlled approach not only enhances safety but also maximizes muscle activation and promotes better muscle growth and strength development.
- Appropriate Weight, When starting goblet squats, begin with a lighter weight to master proper form and technique before progressing to heavier loads. Using too much weight too soon can compromise form and increase the risk of injury. Start with a weight that allows you to perform the exercise with good form for the desired number of repetitions.
- Warm-Up, Always warm up before performing goblet squats to prepare your muscles, joints, and cardiovascular system for the exercise. A proper warm-up increases blood flow to the muscles, improves flexibility, and reduces the risk of injury. Incorporate dynamic stretches, such as leg swings, hip circles, and bodyweight squats, to loosen up the muscles and joints involved in the squatting movement.
By following these detailed safety tips, you can perform goblet squats effectively and safely, reducing the risk of injury while maximizing the benefits of the exercise. Remember to prioritize proper form, control your movements, start with an appropriate weight, and always warm up before beginning your workout. With consistency and attention to safety, goblet squats can be a valuable addition to your fitness routine, helping you build strength, improve muscle tone, and enhance overall fitness levels.
Role of Muscles in Stabilization During Goblet Squat
In the goblet squat, the coordination of various muscle groups is essential to stabilize the body and execute the movement with proper form. Each muscle group contributes to maintaining balance, controlling the descent, and supporting the body's weight throughout the exercise.
The quadriceps, located at the front of the thigh, are primarily responsible for knee extension and provide stability by preventing the knees from collapsing inward. Their activation ensures proper alignment of the lower body and supports the upward movement from the squat position.
The glutes, comprising the gluteus maximus, medius, and minimus, play a critical role in hip stability and power generation. They are activated during the ascent phase of the squat to extend the hips and propel the body upward. Strong glutes not only enhance the effectiveness of the goblet squat but also contribute to overall lower body strength and stability.
Core muscles, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and erector spinae, work synergistically to maintain an upright posture and stabilize the torso throughout the movement. Engaging the core helps prevent excessive forward lean or rounding of the back, ensuring proper spinal alignment and reducing the risk of injury.
The hamstrings, situated at the back of the thigh, assist in controlling the descent phase of the squat and provide stability to the legs. They work in conjunction with the quadriceps to control the movement and maintain balance throughout each repetition.
Finally, the calves play a crucial role in supporting balance and stability, particularly at the bottom of the squat. They help maintain proper ankle alignment and distribute weight evenly across the feet, ensuring a stable base from which to perform the exercise.
Overall, the coordinated effort of these muscle groups is essential for stabilizing the body during the goblet squat and ensuring proper movement mechanics. By strengthening these muscles and improving their coordination, individuals can enhance their performance, reduce the risk of injury, and achieve better results from their workouts.
Conclusion
The goblet squat is a comprehensive exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, promoting strength, stability, and functional fitness. By engaging the lower body, core, and upper body muscles, the goblet squat provides a full-body workout that can enhance overall performance and prevent injuries.
Goblet squats are a highly effective lower body exercise that can help you build strength, improve muscle tone, and enhance overall fitness levels. By focusing on proper form, controlled movements, starting with an appropriate weight, and always warming up before your workout, you can perform goblet squats safely and effectively. With consistent practice and attention to safety, goblet squats can become a valuable addition to your fitness routine, offering numerous benefits such as improved squat mechanics, increased lower body strength, enhanced core stability, and reduced risk of injury. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced athlete, incorporating goblet squats into your workouts can help you achieve your fitness goals and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.